Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) Registration in India
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is a hybrid business structure that combines the benefits of a partnership firm and a company. It provides limited liability protection to partners while allowing them to manage the business flexibly.
LLPs are governed and registered under the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008, which came into effect on 31st March 2008.

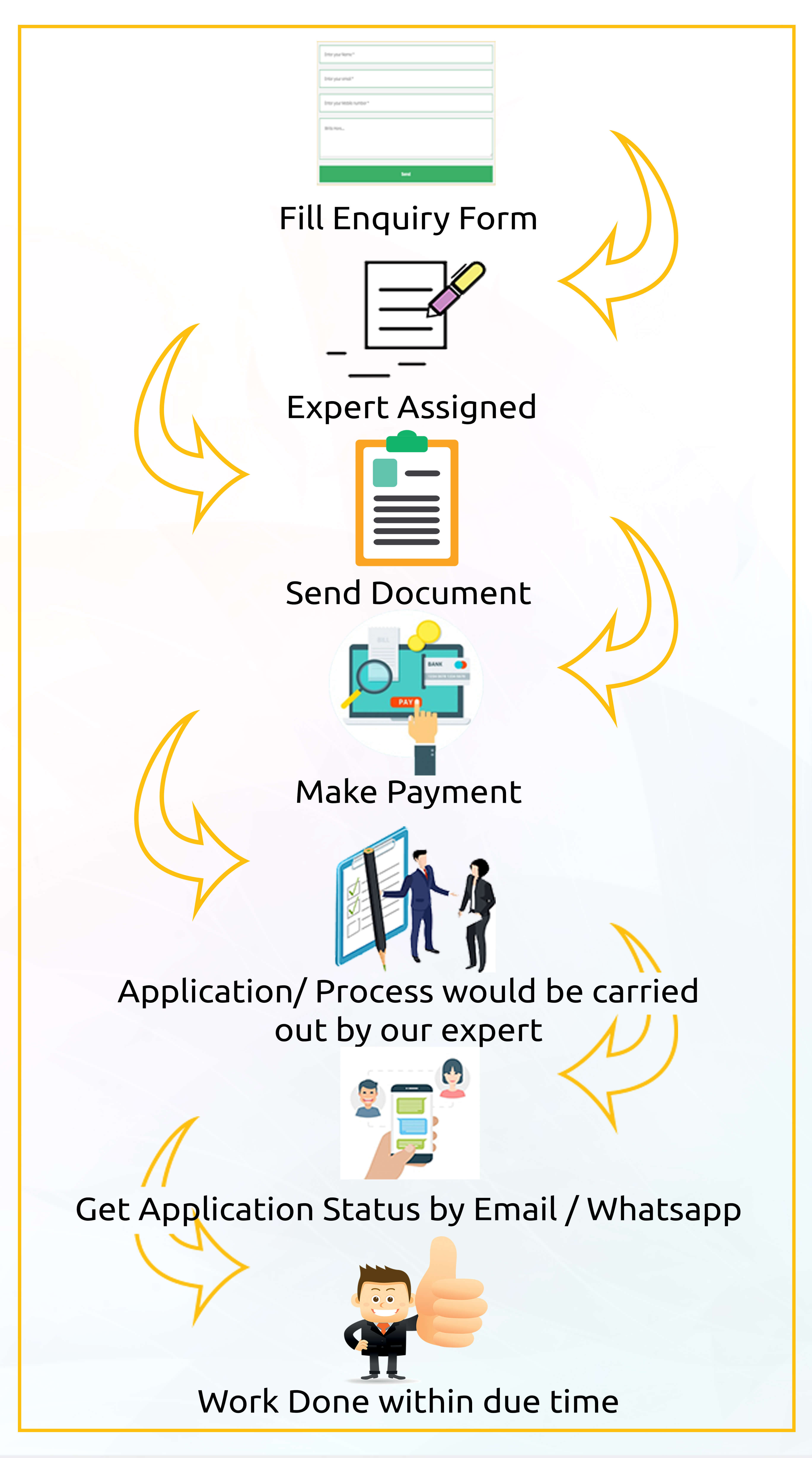
Procedure For Formation Of Limited Liability Partnership Through TaxWare ?
Benefits Of Formation Of Limited Liability Partnership
(A) Easy and Quick Formation
One of the main benefits of LLP is that the process of forming an LLP is easy and not time-consuming like that of a company.
(B) Easy Transferability
The ownership of a LLP can be easily transferred to another person. However, transferee should be inducted as a Designated Partner of the LLP.There are no restrictions upon joining and leaving of partners in LLP.
(C) Separate Legal Existence
An LLP is a Separate legal entity from its Partners in the eyes of law.It can have a PAN number, bank accounts, licenses, approvals, contracts, assets and liabilities in its unique name.
(D) Perpetual succession
According to the provisions of the Act, the LLP will not be winded up in case of death, retirement or insolvency of a partner. The life of the LLP is not affected by the same
(E) Lower Compliance Requirements
According to the provisions of the Act, regulatory compliance is very less in case of LLP as compared to company form of entity
(F) Limited Liability
Partners’ liability of the LLP is limited and it is limited only to their contribution by them to the LLP.No partner can be held responsible for the conduct of other partners.
(G) No Statutory Audit
There is no audit requirement unless the contribution of the LLP exceeds 25 lakh rupees or the turnover of the LLP exceeds 40 lakh rupees annually.
Why Choose a Limited Liability Partnership Over Other Business Structures?
| Business Type | Limited Liability | Easy Fundraising | Separate Legal Entity | Mandatory Audit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sole Proprietorship | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| Partnership | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| LLP (Limited Liability Partnership) | ✅ Yes | ✅ Limited | ✅ Yes | ✅ Only for large LLPs |
| Private Limited Company | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| One Person Company (OPC) | ✅ Yes | ✅ Limited | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |